Spatial Commerce: The New Hot Trend in E-commerce?
06/02/24
6'
In recent years, many trends in e-commerce have emerged (such as voice commerce, metaverse, in-car commerce, etc.); only some of which have materialized. But Spatial Commerce is different and has what it takes to truly revolutionize retail. Above all, it has an ally that can make the decisive difference: Apple.
What exactly is Spatial Commerce? What characterizes it? And what can we expect in the coming years? In the following article, we get to the bottom of these questions and aspects.
What is Spatial Commerce?
Spatial Commerce is based on Spatial Computing
Spatial Commerce, a cutting-edge evolution in online shopping, is deeply rooted in the principles of Spatial Computing (often considered an advanced form of virtual commerce). Spatial Computing is a technology that allows computers to interact with and understand the three-dimensional space around them, integrating the physical and digital worlds. It enables the manipulation of objects in 3D space using inputs like gestures, voice, and environmental data.
This advanced technology is set to revolutionize e-commerce by offering immersive and interactive shopping experiences, blending the physical and digital worlds. Spatial Computing allows consumers to visualize products in a three-dimensional space, which can be either within their actual environment using augmented reality (AR) or in a completely virtual space. This immersive approach enables shoppers to see how items like furniture or clothing would look and fit in their own space or on themselves.
Benefits of Spatial Commerce
The implementation of Spatial Computing in e-commerce not only enhances the realism of online shopping but also leads to more informed purchasing decisions. By allowing customers to virtually ‘try before they buy’, it significantly reduces the likelihood of returns. Moreover, this technology elevates customer engagement and interactivity, offering a personalized and captivating shopping experience. It effectively bridges the gap between physical and online retail, creating a seamless blend of both worlds. As a result, Spatial Commerce is not just an innovative tool for visualization, but a transformative force in reshaping the retail landscape, making shopping more intuitive, engaging, and customer-centric.
What Apple Has to Do With It
Apple’s Vision Pro (basically its VR headset) is a device that marks a significant advancement in the field of spatial computing. As Apple’s first spatial computer, Vision Pro seamlessly integrates digital content with the physical world, offering an immersive experience controlled by natural inputs such as eyes, hands, and voice. This innovative approach allows for a more intuitive and interactive way of computing, transcending traditional screen boundaries. That’s key because it means that one of the strongest companies in the world is backing spatial computer technology.
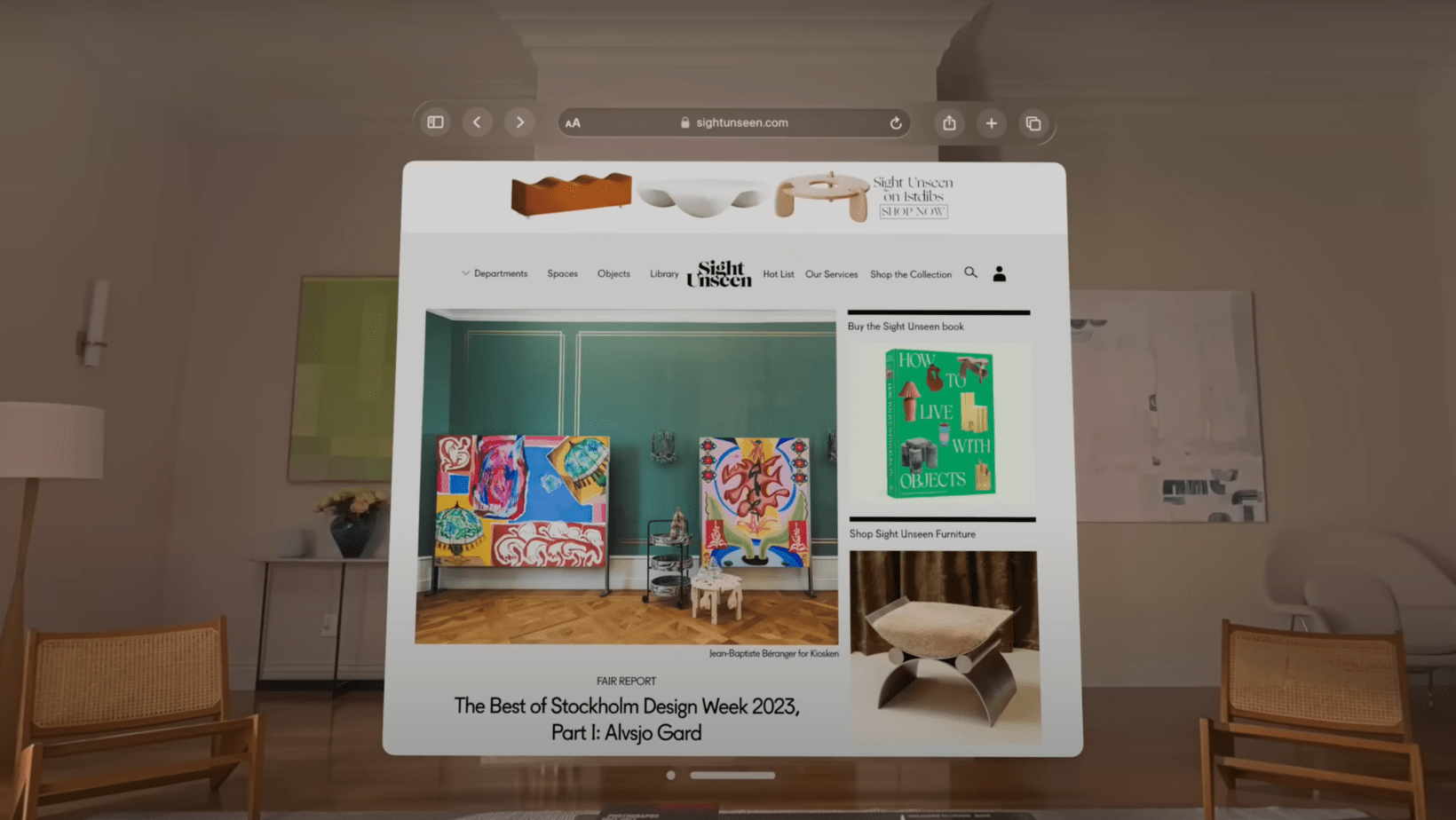
An e-commerce website was prominently featured in the product presentation of the Apple Vision Pro (Image credit: Apple).
A recent exploration into the capabilities of Apple’s Vision Pro has revealed its initial practical application in the realm of e-commerce. This was demonstrated through a navigation experience to an e-commerce site, specifically designed by HumanNYC, a Shopify agency.
This instance is noteworthy as it illustrates how even advanced VR technologies like the Vision Pro are being used to enhance familiar activities such as online shopping. However, the approach taken by Vision Pro marks a significant shift in the medium. The traditional concept of a screen, typically held in hand or placed on a desk, is transformed. With Vision Pro, the display becomes an integral part of the user’s visual field, positioned just inches from the eyes. This shift redefines the user’s interaction with e-commerce platforms.
Apple’s vision for the future, as demonstrated by the Vision Pro, currently focuses on presenting a floating website window as the primary interface for e-commerce interactions, rather than creating a virtual showroom filled with 3D models of products like furniture. This approach indicates a blending of familiar online shopping experiences with the immersive capabilities of spatial computing.
Even if Apple’s VR headset is likely to see smaller sales figures and slower sales growth compared to previous product launches, the race for spatial commerce is set.
Shopping on Apple’s Vision Pro (after launch)
Following the official launch of Vision Pro at the beginning of 2024, there are now some interesting app examples from brands.
The adoption of Apple’s spatial computing headset in the retail sector is marked by innovative approaches from brands like Alo Yoga or E.l.f Cosmetics. Alo Yoga’s app, designed in collaboration with Obsess, offers a combined experience of wellness and shopping, set in a virtual environment that simulates nature. It showcases its products in a new innovative environment which encourages purchase. E.l.f Cosmetics’ application, on the other hand, integrates gaming elements with product discovery, aiming to provide a playful yet informative experience. These developments represent a significant shift in how mixed-reality technology is being utilized to enhance consumer engagement in retail.
Examples of Spatial Commerce
Classic examples
For now AR or Mixed Reality applications have often been feasible only for major brands. Brands like Sephora have been using AR features to try makeup on one’s face, and Ikea and Amazon have allowed users to place items from their store in their surroundings for quite a while.
Sephora has adopted spatial commerce through a VR makeup try-on feature, allowing customers to virtually test products on their faces in real-time, aiding in more informed purchases. Similarly, Ikea‘s VR app lets customers visualize furniture in their rooms with 98% accuracy, including a 3D room planner and virtual showroom for layout and style experimentation, enhancing the shopping experience and boosting customer satisfaction and sales.
However, these have often been complex in-house developments, not affordable or feasible for all brands or retailers.
Changes through generative AI
Spatial Computing applications are gradually becoming available to everyone. Generative AI is laying the foundation for many immersive, spatial experiences in shopping, and in the discovery phase, it’s driving Spatial Computing forward by making AI-powered AR or VR scenarios affordable. Similarly, major platforms are advancing the development by implementing Spatial Computing features.
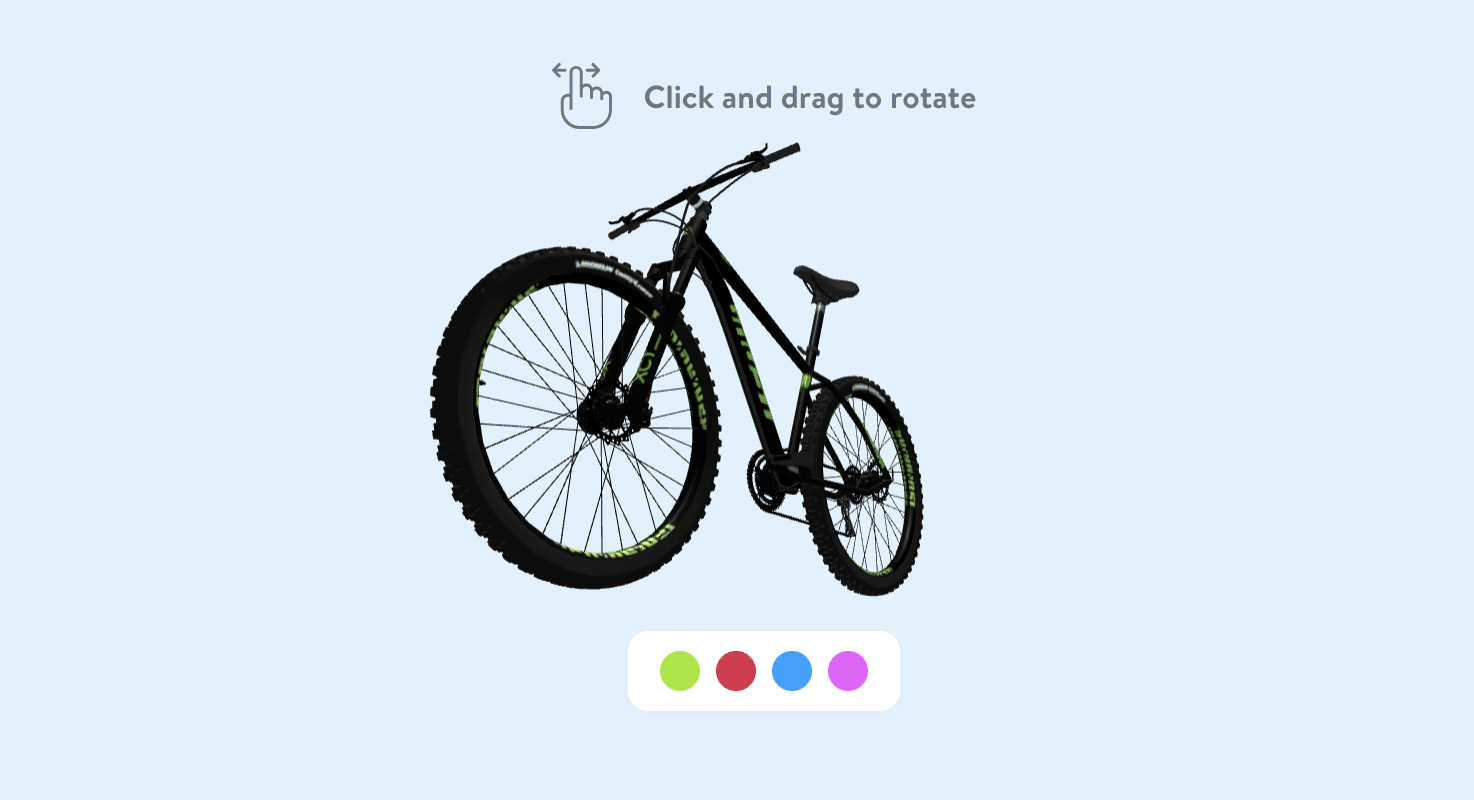
Spatial Commerce accordingly to Shopware (Image credit: Shopware).
One example here is Shopware. The e-commerce platform is now implementing Spatial Computing, making the use and creation of 3D visuals with AI and machine learning easier and faster for brands. Shopware’s new feature seeks solutions to these questions: How can we display products from every angle without multiple clicks? Is it possible to integrate products into real-life scenarios on their pages? And, can we equip merchants with advanced tools for virtual shopping using futuristic devices not yet developed?
Shopify, a rival in the market, is showcasing innovative Spatial Commerce applications beyond mere product presentation on its Github’s Spatial Commerce Projects section. A notable concept from the Canadian ecommerce platform is an immersive furniture assembly guide. Although demonstrated with Meta Quest, this application can be effectively operated using an AR feature and a smartphone camera.
Google and Microsoft are also embedding spatial computing features into their search engines, broadening access for various brands and retailers. This advancement eliminates the need for costly proprietary development. As this technology garners more attention, it’s becoming a staple in everyday user experiences. Customers will soon demand pre-purchase virtual makeup trials and more. While currently perceived as a novelty, Spatial Computing is rapidly evolving from a competitive edge to an essential tool for businesses.
(Cover image credit: Apple)
Your e-commerce library
E-commerce for Retailers
Learn moreE-commerce for Brands
Learn moreL'Oréal Luxe Success Story
Learn moreSign up for our newsletter
By submitting this form you authorize Lengow to process your data for the purpose of sending you Lengow newsletters . You have the right to access, rectify and delete this data, to oppose its processing, to limit its use, to render it portable and to define the guidelines relating to its fate in the event of death. You can exercise these rights at any time by writing to dpo@lengow.com

Trending Posts
Marketing channels
Where does Gen Z shop online?
Gen Z online shopping is transforming the digital marketplace, setting trends that redefine what it means to engage with brands…
16/04/24
9'
Marketplaces
The Top 10 Marketplaces in Europe
The e-commerce scene is a vibrant mix of marketplaces in Europe. These aren't just websites; they're bustling hubs where millions…
08/12/23
7'
Marketplaces
Lengow Now Fully Supports Zalando Logistics Solutions ZSS and ZRS
Zalando, one of Europe’s leading fashion marketplaces, continues to raise the bar with its advanced logistics and fulfillment programs. After…
12/12/24
4'
Marketplaces
How to win the Buy Box on Marketplaces (Amazon, Zalando, etc.)
What is the most important thing for marketplace sellers? Exactly, the Buy Box! If you don't have the Buy Box…
02/04/24
10'
Marketplaces
How to Sell on Temu? Best Tips
Emerging under the vast umbrella of PDD Holdings Inc., Temu has skyrocketed in popularity as a shopping sensation from China…
17/08/23
5'




